
- #PARALLEL TO SERIAL CONVERTER USING D FLIP FLOP TINYCAD HOW TO#
- #PARALLEL TO SERIAL CONVERTER USING D FLIP FLOP TINYCAD SERIES#
How can we give two distinct signals to the same port? What can we use that would allow us to select from one of the two inputs that need to be given to the flip-flops? The input ports need their separate input line as well as a connection from the previous flip-flops. This means that the outputs of flip-flops (Q ports) will also need to be connected to the inputs (D ports) of their subsequent flip-flops.
#PARALLEL TO SERIAL CONVERTER USING D FLIP FLOP TINYCAD SERIES#
Moreover, the data needs to move through the series of flip-flops. And the title also requires us to have serial outputs.įrom the preceding designs, we have seen that a serial output means that data has to be taken out from only the final flip-flop. The title requires us to have parallel inputs, which means that all the D ports will have their own independent input lines.
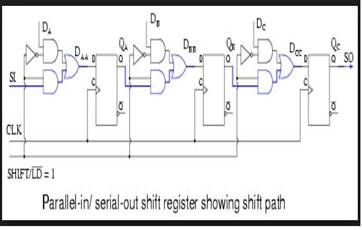
Mostly due to the fact that we need to share ports in order to achieve this configuration.
#PARALLEL TO SERIAL CONVERTER USING D FLIP FLOP TINYCAD HOW TO#
4-bit PIPO shift register How to design a 4-bit Parallel in Serial Out shift register (PISO)? The resulting logic circuit for the 4-bit PIPO shift register is as follows. Hence, we will connect the input ports (D ports) of the flip-flops to the input pins.Įventually, we will connect the clock ports to the clock input and the reset ports to the reset inputs. The name suggests that we have parallel inputs too.
Let’s straightaway connect the output ports (Q ports) of the D flip-flops to the output pins. 4-bit SIPO shift register How to design a 4-bit Parallel in Parallel Out shift register (PIPO)?Īgain repeating the same approach we saw earlier, we will go ahead with cues from the title.
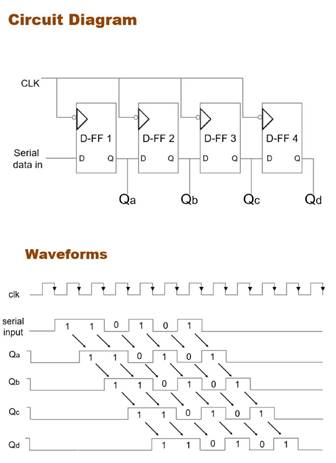
That settles the serial input part.įinally, apply the clock and the reset signal and voila you have your 4-bit SIPO shift register. Connect all the remaining flip-flops’ outputs to their subsequent flip-flops’ input. Similarly, take a single output from the last flip-flop. Give a single input to the first flip-flop. Let’s take the four D flip-flops and take outputs from each individual flip-flop. The timing diagram of data shift through a 4-bit SISO shift register How to design a 4-bit Serial In Parallel Out shift register (SIPO)? Furthermore, at the fourth clock pulse, we will get the 1-bit data “1” at the output Q4, having undergone a successful shift. In the next clock cycle it will be taken as input by the D2 flip-flop and will be available at Q2 output and so on. This input port is to the first flip-flop in the register. Since we have a serial input, we will take only one input port. And all of them have the same reset input. Okay, so we know that we have four D flip-flops. How to design a 4-bit Serial In Serial Out shift register (SISO)? To convert between serial-parallel – Since we have both serial and parallel types of inputs and outputs, we can use shift registers to convert serial data to parallel or vice versa.So we can use them to introduce some delay if we need it. Either way, the processes consume some clock cycles. To produce a delay – The data can stay inside the shift register or pass through it.In the absence of a clock pulse, the shift register holds that data. To store data – The flip-flops shift data on the application of a clock pulse.In this post, we will look at shift registers where the data moves in the right direction. To shift data – Shift registers can shift data either to the right, to the left or in both directions.The types of inputs and outputs of these four categories are evident from their names. Doing that, we get four main configurations. We can classify shift registers depending on these two data flow methods. So we have two ways in which data can ‘flow’ through a shift register. Similarly, each flip-flop can have its own output too. This particular setting of giving input is known as parallel input. Parallel: Each flip-flop can have its own input.The output is in the same order as the input. We get the data output at the last flip-flop. Each bit passes through the cascade in a line. Serially: Data enters the cascade of flip-flops in a stream.We can feed and extract data to and from a shift register in two ways: Commonly available Shift Register ICs (source) How do shift registers move data?.Some commonly available shift registers.How to design a 4-bit Parallel in Serial Out shift register (PISO)?.How to design a 4-bit Parallel in Parallel Out shift register (PIPO)?.How to design a 4-bit Serial In Parallel Out shift register (SIPO)?.How to design a 4-bit Serial In Serial Out shift register (SISO)?.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
